If you have feedback, let us know.
IPCCC ICD-11 Congenital Heart Atlas
- Structural developmental anomaly of heart or great vessels
- Congenital anomaly of position or spatial relationships of thoraco-abdominal organs
- Anomalous position-orientation of heart
- ■ Usual atrial arrangement
- Abnormal atrial arrangement
- Abnormal ventricular relationships
- Abnormal relationship of great arterial roots
- ■ Aortic root directly anterior to pulmonary root
- ■ Aortic root anterior and rightward to pulmonary root
- ■ Aortic root anterior and leftward to pulmonary root
- ■ Aortic root side by side and directly rightward to pulmonary root
- ■ Aortic root side by side and directly leftward to pulmonary root
- ■ Aortic root directly posterior to pulmonary root
- ■ Aortic root posterior and rightward to pulmonary root
- ■ Aortic root posterior and leftward to pulmonary root
- Abnormal intrapericardial course of great arteries
- Visceral heterotaxy
- ■ Total mirror imagery
- Congenital anomaly of an atrioventricular or ventriculo-arterial connection
- ■ Concordant atrioventricular connections
- Discordant atrioventricular connections
- Transposition of the great arteries
- ■ Transposition of the great arteries with concordant atrioventricular connections and intact ventricular septum
- ■ Transposition of the great arteries with concordant atrioventricular connections and ventricular septal defect
- ■ Transposition of the great arteries with concordant atrioventricular connections and ventricular septal defect and left ventricular outflow tract obstruction
- Concordant ventriculo-arterial connections
- Double outlet right ventricle
- Double outlet right ventricle with subaortic or doubly committed ventricular septal defect and pulmonary stenosis, Fallot type
- ■ Double outlet right ventricle with subpulmonary ventricular septal defect, transposition type
- ■ Double outlet right ventricle with non-committed ventricular septal defect
- Double outlet right ventricle with subaortic or doubly committed ventricular septal defect without pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect type
- ■ Double outlet right ventricle with intact ventricular septum
- ■ Double outlet left ventricle
- Common arterial trunk
- Congenital anomaly of mediastinal vein
- Congenital anomaly of mediastinal systemic vein
- Congenital anomaly of pulmonary vein
- Anomalous pulmonary venous connection
- ■ Congenital pulmonary venous stenosis or hypoplasia
- ■ Congenital atresia of pulmonary vein
- Congenital anomaly of an atrium or atrial septum
- Congenital anomaly of an atrioventricular valve or atrioventricular septum
- Congenital anomaly of tricuspid valve
- ■ Congenital tricuspid regurgitation
- ■ Congenital tricuspid valvar stenosis
- ■ Tricuspid annular hypoplasia
- ■ Dysplasia of tricuspid valve
- ■ Straddling tricuspid valve
- ■ Overriding tricuspid valve
- ■ Ebstein malformation of tricuspid valve
- ■ Absent tricuspid valve leaflet
- ■ True cleft of tricuspid valve leaflet
- Congenital anomaly of mitral valve
- ■ Congenital mitral regurgitation
- ■ Congenital mitral valvar stenosis
- ■ Mitral annular hypoplasia
- ■ Straddling mitral valve
- ■ Overriding mitral valve
- ■ Dysplasia of mitral valve
- Supravalvar or intravalvar mitral ring
- ■ Congenital mitral valvar prolapse
- ■ True cleft of anterior mitral leaflet
- Congenital anomaly of mitral subvalvar apparatus
- ■ Accessory tissue on mitral valve leaflet
- ■ Congenital unguarded mitral orifice
- ■ Double orifice of mitral valve
- ■ Congenital anomaly of left-sided atrioventricular valve in double inlet ventricle
- ■ Congenital anomaly of right-sided atrioventricular valve in double inlet ventricle
- Common atrioventricular junction
- Common atrioventricular junction with atrioventricular septal defect
- ■ Atrioventricular septal defect with balanced ventricles
- Atrioventricular septal defect with ventricular imbalance
- ■ Atrioventricular septal defect with communication at the atrial level only
- ■ Atrioventricular septal defect with communication at the ventricular level only
- ■ Atrioventricular septal defect with communication at atrial level and restrictive communication at ventricular level
- ■ Atrioventricular septal defect with communication at atrial level and unrestrictive communication at ventricular level
- ■ Atrioventricular septal defect and tetralogy of Fallot
- ■ Common atrium with common atrioventricular junction
- ■ Common atrioventricular valvar regurgitation
- Atypical common atrioventricular valve
- ■ Common atrioventricular junction without an atrioventricular septal defect
- Common atrioventricular junction with atrioventricular septal defect
- ■ Communication between left ventricle and right atrium
- Congenital anomaly of tricuspid valve
- Congenital anomaly of a ventricle or the ventricular septum
- Congenital right ventricular anomaly
- Congenital left ventricular anomaly
- ■ Anomalous ventricular bands
- Congenital anomaly of ventricular septum
- ■ Restrictive interventricular communication when an interventricular shunt is physiologically necessary
- Ventricular septal defect
- ■ Perimembranous central ventricular septal defect
- Inlet ventricular septal defect without a common atrioventricular junction
- ■ Inlet perimembranous ventricular septal defect without atrioventricular septal malalignment without a common atrioventricular junction
- ■ Inlet perimembranous ventricular septal defect with atrioventricular septal malalignment and without a common atrioventricular junction
- ■ Inlet muscular ventricular septal defect
- Trabecular muscular ventricular septal defect
- Outlet ventricular septal defect
- Outlet ventricular septal defect without malalignment
- Outlet ventricular septal defect with anteriorly malaligned outlet septum
- Outlet ventricular septal defect with posteriorly malaligned outlet septum
- ■ Ventricular septal defect haemodynamically insignificant
- ■ Multiple ventricular septal defects
- Functionally univentricular heart
- Congenital anomaly of a ventriculo-arterial valve or adjacent regions
- Congenital anomaly of pulmonary valve
- ■ Congenital subpulmonary stenosis
- ■ Congenital supravalvar pulmonary stenosis
- Congenital pulmonary atresia
- Congenital anomaly of aortic valve
- Congenital subaortic stenosis
- ■ Congenital supravalvar aortic stenosis
- ■ Aneurysm of aortic sinus of Valsalva
- Aortoventricular tunnel
- Congenital anomaly of great arteries including arterial duct
- ■ Congenital aortopulmonary window
- Congenital anomaly of pulmonary arterial tree
- ■ Congenital dilation of pulmonary arterial tree
- Congenital pulmonary trunk anomaly
- Congenital pulmonary arterial branch anomaly
- Congenital pulmonary arterial branch stenosis
- Congenital pulmonary arterial branch hypoplasia
- Absent or atretic right or left pulmonary artery
- ■ Congenital central pulmonary arterial stenosis or hypoplasia proximal to hilar bifurcation
- ■ Congenital peripheral pulmonary arterial stenosis or hypoplasia at or beyond hilar bifurcation
- ■ Congenitally discontinuous, non-confluent right and left pulmonary arteries
- Pulmonary artery origin from ascending aorta
- Pulmonary artery from arterial duct
- Congenital anomaly of aorta or its branches
- Congenital anomaly of ascending aorta
- Congenital anomaly of aortic arch
- Coarctation of aorta
- Congenital anomaly of aortic arch branch
- Congenital anomaly of descending thoracic or abdominal aorta
- Tracheo-oesophageal compressive syndrome
- Vascular Ring
- ■ Anomalous origin of left pulmonary artery from right pulmonary artery
- Congenital arterial duct anomaly
- ■ Systemic-to-pulmonary collateral arteries
- Congenital anomaly of coronary artery
- Anomalous origin of coronary artery from pulmonary arterial tree
- Anomalous aortic origin or course of coronary artery
- ■ Myocardial bridging of coronary artery
- ■ Congenital coronary arterial orifice stenosis
- ■ Congenital coronary arterial orifice atresia
- Congenital coronary arterial fistula
- ■ Congenital coronary arterial aneurysm
- ■ Accessory coronary artery
- ■ Congenital absence of coronary artery
- ■ Coronary arterial hypoplasia
- Congenital pericardial anomaly
- ■ Congenital cardiac tumour
- ■ Pulmonary arteriovenous fistula
- ■ Bifid apex of heart
- Congenital anomaly of position or spatial relationships of thoraco-abdominal organs
You are here: Right isomerism ⇗ Visceral heterotaxy ⇗ Congenital anomaly of position or spatial relationships of thoraco-abdominal organs ⇗ Structural developmental anomaly of heart or great vessels
| IPCCC Term | Right isomerism |
| IPCCC Code | 03.01.04 |
| ICD-11 MMS | LA83 |
| ICD-11 Code | 1576694141 |
Definition
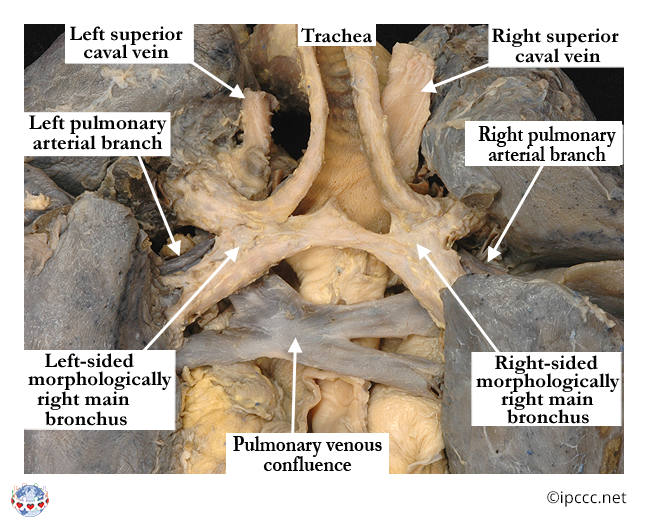
A congenital cardiovascular malformation that is a variant of heterotaxy syndrome in which some paired structures on opposite sides of the left-right axis of the body are symmetrical mirror images of each other and have the morphology of the normal right-sided structures.
Synonyms/Abbreviations
Bilateral right-sidedness; Ivemark syndrome; Asplenia syndrome; Splenic agenesis syndrome
STS-EACTS-derived IPCCC term
Syndrome, Heterotaxy (heterotaxy syndrome) (visceral heterotaxy)-modifier, Isomerism, Right isomerism
EPCC-derived IPCCC term
Right isomerism
ICD-11 MMS code or crossmap
LA83
ICD-10 MMS code or crossmap
Q20.6**: This term is not in ICD-10. If coding using ICD-10, crossmap to higher order ICD-10 term “Isomerism of atrial appendages” with code Q20.6
Parent
Visceral heterotaxy
Siblings
Coding Notes
None

 Anatomic Specimen
Anatomic Specimen  Diagrams
Diagrams  Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram  CT-MRI
CT-MRI  Angiography
Angiography  Surgical Images
Surgical Images